SAP S/4HANA Profit Center | Table CEPC
Profit center master data table in SAP
The profit center master data table in SAP is CEPC, and the corresponding long texts are stored in table CEPCT.
See below the definition of a profit center, where to find in SAP table viewer the contents of the table tables storing the SAP profit center data, and also where to create a profit center in SAP.
Important SAP Profit Center Table in SAP CO (EC-PCA)Definition of Profit Center in SAP CO
A profit center is an organizational unit in accounting that reflects a management-oriented structure of the organization for the purpose of internal control.
You can analyze operating results for profit centers using either the cost-of-sales or the period accounting approach.
By calculating the fixed capital as well, you can use your profit centers as investment centers.
In the SAP profit center table you will find the different parts of the organization that are allowed to reporting group profits, for example the internal services of the various business units of a company.
Therefore, the profit center table in SAP will be a central point of reporting and system organization, and profit center accounting in SAP S4 HANA is a central point of interest for Financial consultants, Controlling analysts, and in the SAP FICO business processes.
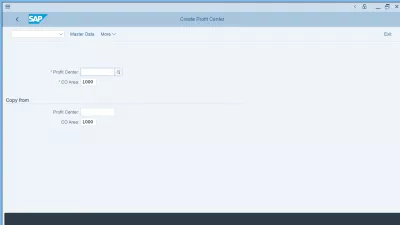
SAP library profit center master dataCreate a profit center in SAP
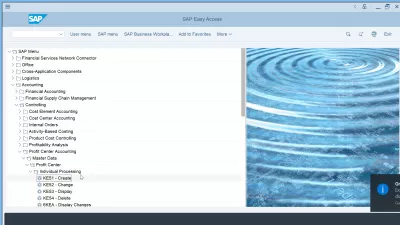
To create a profit center in SAP, navigate in the SAP tree to accounting > controlling > profit center accounting > master data > profit center > individual processing > tcode KE51 create profit center.
The transaction code to create profit center in SAP is KE51 create profit center.
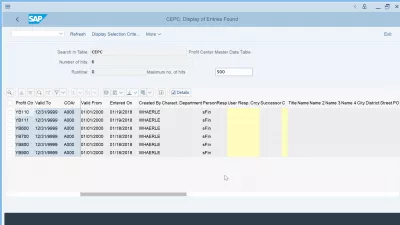
SAP Profit Center Master Data Table
- CEPC-PRCTR, Profit Center: Key which together with the controlling area uniquely identifies a profit center.
- CEPC-DATBI, Valid To: Date indicating up to when an entry is valid.
- CEPC-KOKRS, Controlling Area: Uniquely identifies a controlling area.
The controlling area is the highest organizational unit in Controlling.
- CEPC-DATAB, Valid From: Date indicating as of when an entry is valid.
- CEPC-ERSDA, Entered On: Date on which the cost estimate was created.
- CEPC-USNAM, Created By: User ID of the person who created the cost estimate.
- CEPC-MERKMAL, Field name of CO-PA characteristic: Field name of CO-PA characteristic.
- CEPC-ABTEI, Department: This field contains the name of the department to which the profit center belongs.
- CEPC-VERAK, Person Responsible for Profit Center: Name of the person in charge of the profit center.
- CEPC-VERAK_USER, User Responsible: In this field, you can enter the user ID of the person responsible for the profit center. This user ID is stored in the SAP user master record.
- CEPC-WAERS, Currency: Currency key for amounts in the system.
- CEPC-NPRCTR, Successor profit center: Successor profit center.
- CEPC-LAND1, Country Key: The country key contains information which the system uses to check entries such as the length of the postal code or bank account number.
- CEPC-ANRED, Title: Title of the customer/vendor.
- CEPC-NAME1, Name 1: Name 1 of the customer/vendor address.
- CEPC-ORT01, City: Name of the city as a part of the address.
- CEPC-ORT02, District: Supplement to city name or district.
- CEPC-STRAS, Street: Street and house number as part of the address.
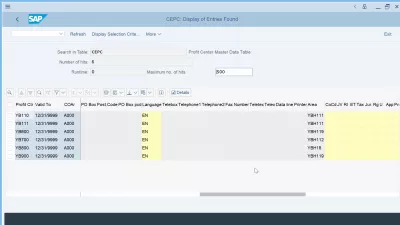
- CEPC-PFACH, PO Box: Post office box.
- CEPC-PSTLZ, Postal Code: This field contains the postal (zip) code for the house address (street and city).
- CEPC-PSTL2, P.O. Box Postal Code: Postal code needed to allocate the P.O. Box.
- CEPC-SPRAS, Language Key: The language key indicates:
- the language in which texts are displayed,
- the language in which you enter texts,
- the language in which the system prints texts.
- CEPC-TELBX, Telebox number: Number of telebox for electronic mail.
- CEPC-TELF1, Telephone 1: Primary phone number.
- CEPC-TELF2, Telephone 2: Secondary phone number.
- CEPC-TELFX, Fax Number: Number under which a business partner's telefax machine can be reached.
- CEPC-TELTX, Teletex number: Number under which a business partner's teletex machine can be reached.
- Teletex is a service for the transmission of text and data. In comparison with a telex, however, the transmission times of teletex messages are shorter and the range of characters available is greater.
- CEPC-TELX1, Telex number: Number under which the telex machine can be reached.
- CEPC-DATLT, Data line: Line number (telephone line). Dialing this number enables you to establish a link with another computer at a different location.
- CEPC-DRNAM, Printer name: Printer name for profit center.
- CEPC-KHINR, Hierarchy Area: The standard hierarchy is a tree structure which displays the organization of all the profit centers in one controlling area.
The structural elements in the standard hierarchy are the profit center area and the summarization area.
The profit center area is an end point in the tree structure which is not at the top and can have profit centers assigned to it when you maintain the standard hierarchy.
The summarization area is used to summarize the data on the profit centers beneath it, although it does not itself contain any profit centers.
By definition, the system always regards the profit center hierarchy which was entered when the controlling area was created as the standard hierarchy.
- CEPC-BUKRS, Company Code: The company code is an organizational unit within financial accounting.
- CEPC-VNAME, Joint venture: A joint venture in the SAP system is a summarization of cost objects whose costs are split up among partners.
A joint venture is usually lead by an operating authority, who is responsible for the costs incurred. At the end of a period, all of the costs incurred are split up and allocated to the partners involved.
Joint ventures are created to keep costs as low as possible for the operating authority and the partners. This is achieved by distributing the costs incurred to the participants of the joint venture.
- CEPC-RECID, Recovery Indicator: In global companies that belong to joint ventures, incurred costs are usually shared among different recovery indicators which can then be dealt with in different ways using the periodic settlement program.
You can define recovery indicators at three different levels:
- Document type,
- You can assign a recovery indicator to each document type for the credit side and for the debit side. These recovery indicators are internal recovery indicators and are defined in a separate system table.
- Cost element (primary and secondary),
- Cost object.
When you make a posting in one of the feeder systems of the Joint Venture Accounting System, all three levels are evaluated in the sequence defined. The first recovery indicator found is transferred to the Joint Venture Accounting System.
- CEPC-ETYPE, Equity type: Equity type.
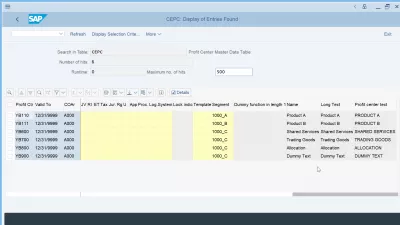
- CEPC-TXJCD, Tax Jurisdiction: The tax jurisdiction is used for determining the tax rates in the USA. It defines to which tax authorities you must pay your taxes. It is always the city to which the goods are supplied.
- CEPC-REGIO, Region: In some countries, the region forms part of the address. The meaning depends on the country.
- CEPC-KVEWE, Usage: Determines for which area the condition is used (for example, pricing or output).
- CEPC-KAPPL, Application: Subdivides the usage of a condition (for example, pricing) for use in different application areas (for example, sales & distribution or purchasing).
- CEPC-KALSM, Procedure: Specifies the conditions that are allowed for a document and defines the sequence in which they are used.
- CEPC-LOGSYSTEM, Logical System: System in which integrated applications are running on a common data basis.
The distribution of data between systems requires that each system in the network has a unique identification. Logical systems are used for this purpose.
- CEPC-LOCK_IND, Lock indicator: You can use the lock indicator to lock a profit center for postings. The lock only applies to the selected time interval. If the profit center is assigned to an object that receives a posting, the system displays an error message and the data is not posted.
- CEPC-PCA_TEMPLATE, PrCtr Formula Planning Template: Contains funtions, which are used to find plan values using formula planning.
- CEPC-SEGMENT, Segment: Segment for segmental reporting.
- CEPC-EEW_CEPC_PS_DUMMY, Dummy function in length 1: Dummy function in length 1.
- CEPC-Name, Name: General description of the object.
- CEPC-Long Text, Long Text: A text that describes the object to which it refers in greater detail.
- CEPC-Profit center short text for matchcode, Profit center short text for matchcode: Search term for matchcode search.
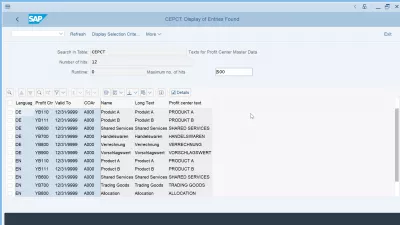
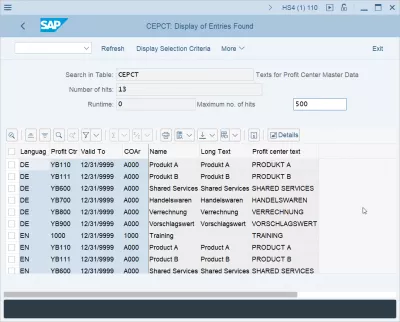
Profit center description table in SAP CEPCT
The profit center description table in SAP is the table CEPCT Texts for Profit Center Master Data, and contains the following fields:
- CEPCT-SPRAS: Language
- CEPCT-PRCTR: SAP Profit Center table link
- CEPCT-DATBI: Valid To date
- CEPCT-KOKRS: CO area (Controlling Area)
- CEPCT-KTEXT: Profit Center description name
- CEPCT-LTEXT: Profit Center description long text
- CEPCT-MCTXT: Profit Center description text
Frequently Asked Questions
- How to create profit center in SAP?
- To create such a center in SAP, navigate in the SAP tree to Accounting > Controlling > Profit Center Accounting > Master Data > Profit Center > Individual Processing > tcode KE51 create Profit Center. The transaction code for creating a profit center in SAP is KE51 create profit center.
- What is the significance of Table CEPC in SAP S/4HANA Profit Center?
- Table CEPC in SAP S/4HANA holds profit center data, essential for financial reporting and controlling.
Intro to SAP HANA for Non-Techies in video

Yoann Bierling is a Web Publishing & Digital Consulting professional, making a global impact through expertise and innovation in technologies. Passionate about empowering individuals and organizations to thrive in the digital age, he is driven to deliver exceptional results and drive growth through educational content creation.